Workspace provider management
This article walks you through the process of managing your workspace provider via the Coder UI.
Admin UI
Site admins and site managers can view the workspace providers configuration page available via Manage > Workspace Providers.
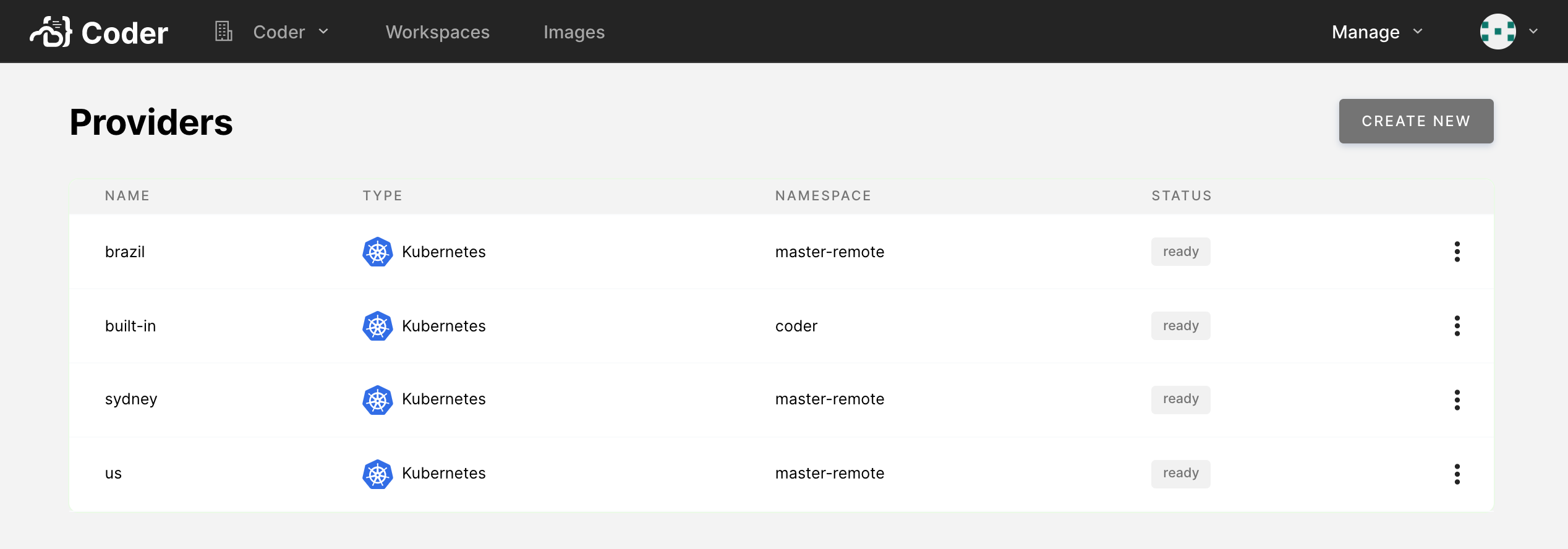
The Admin panel shows an overview of all configured workspace providers and indicates their statuses and details.
Statuses
A workspace provider can have one of the following statuses:
- Pending: The workspace provider has been registered but not deployed to the remote Kubernetes cluster.
- Ready: The workspace provider is online and available, and you can provision new workspaces to it.
- Error: The workspace provider encountered an issue on startup or cannot be reached by the Coder deployment. The workspace provider's details will include an error message.
Edit a workspace provider
To edit a workspace provider, log in to Coder, and go to Manage > Providers.
In the Providers list, find the workspace provider you want to edit. Click the vertical ellipsis to its right, and select Edit.
At this point, you can:
-
Change the name of the provider.
-
Select the organizations that can use this provider; if you do not select at least one organization, no one will be able to provision workspaces using this provider.
Organizations must not contain any workspaces in the workspace provider before you remove them from a workspace provider's allowlist.
-
Change the features of the workspace provider. You can:
-
Enable end-to-end encryption for this provider
-
Enable external SSH connections to the provider's workspaces via the Coder CLI
-
Specify an Access URL that will be used only by workspaces deployed to this provider instead of the site-wide access URL for the deployment
-
Specify a Kubernetes storage class to use when Coder provisions workspaces (this is useful for improving disk performance)
-
Specify the Kubernetes service account that Coder uses to provision workspaces
If you enable end-to-end encryption, end-users using SSH need to rerun
coder config-ssh. -
-
Specify the CVM internal network. CVMs use an internal bridge network to communicate with the outside world. The default network range used is
172.19.0.0/30. If this overlaps with existing resources in your network, you can specify an alternative network range here in CIDR format. This setting applies to both cached and non-cached CVMs, but does not affect non-CVM workspaces.The CIDR must allow for 2 hosts at minimum, so a
/30network is the smallest possible network. Larger networks are acceptable. -
Specify the Kubernetes
pod_tolerations,pod_node_selector,service_account_annotations, andaffinityfor the workspaces deployed with this provider:{ "pod_tolerations": [ { "key": "com.coder.workspace", "operator": "Exists", "effect": "NoSchedule" } ], "pod_node_selector": {}, "service_account_annotations": {}, "affinity": {} }Configuring service account annotations allows you to create Kubernetes service accounts for each workspace and attach custom annotations to the service account. This is commonly used to integrate OIDC authentication into the workspace pods.
To set service account annotations, the RBAC role for the Coder workspace provider must have the correct permissions for controlling the service accounts resource. See Creating a Kubernetes Workspace Provider for information on role required.
The annotations can use
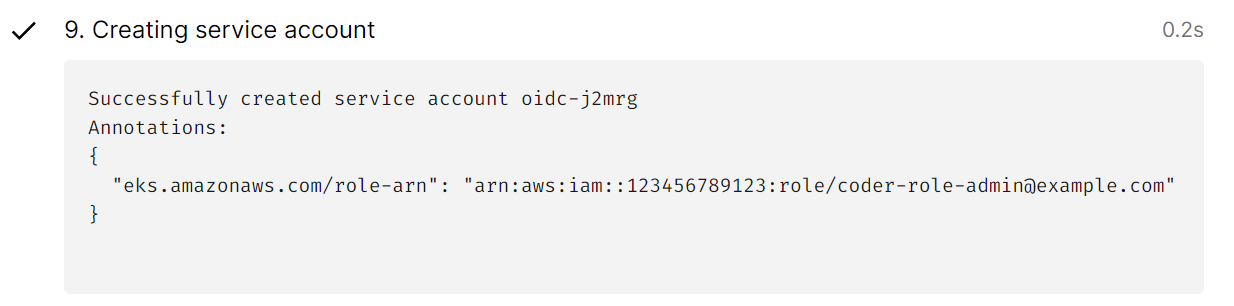
{{ .UserEmail }}to render the workspace user's email:{ "service_account_annotations": { "eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn": "arn:aws:iam::123456789123:role/coder-role-{{.UserEmail}}" } }Currently, any changes made to the workspace container via mutating webhooks will not propagate to CVM workspaces. As such, environment variables and files injected by authentication providers will be missing.
Once set, you will see a workspace build set where a service account is created and the user email is populated properly.
Configuring affinities allows you to control how workspaces are scheduled across nodes. By default, Coder sets a default pod affinity that favors scheduling pods on Nodes that have other workspaces running to optimize for cost savings. The default affinity is the following:
"affinity": { "podAffinity": { "preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution": [ { "weight": 1, "podAffinityTerm": { "labelSelector": { "matchLabels": { "com.coder.resource": "true" } }, "topologyKey": "kubernetes.io/hostname" } } ] } }For Kubernetes clusters with nodes spread across multiple availability zones, it may not be favorable to use Coder's default
affinity. Because persistent disks are often zonal, this can cause pods to become saturated in a single zone and become unschedulable. You can unset this affinity by setting it to an empty object and allow the default behavior of the Kubernetes scheduler."affinity": {}
Once you've made your changes, click Update Provider to save and continue.
Delete a workspace provider
-
Log in to Coder, and go to Manage > Workspace providers.
-
In the Providers list, find the workspace provider you want to delete. Click the vertical ellipsis to its right. Select Delete.
-
Confirm that you want to delete the provider; once deleted, no user will be able to provision workspaces using that provider.
You can only remove a workspace provider if it no longer contains any workspaces, so you must remove all workspaces before deleting the workspace provider.